Ethereum Bitcoin Price Usd Trends And Investment Insights
Beginning with ethereum bitcoin price usd, the narrative unfolds in a compelling and distinctive manner, drawing readers into a story that promises to be both engaging and uniquely memorable.
As two of the most significant cryptocurrencies in the market, Ethereum and Bitcoin have their own unique origins, technologies, and purposes. Understanding their current pricing dynamics is crucial for investors and enthusiasts alike, as both currencies have exhibited fascinating trends and fluctuations in recent times.
Introduction to Ethereum and Bitcoin
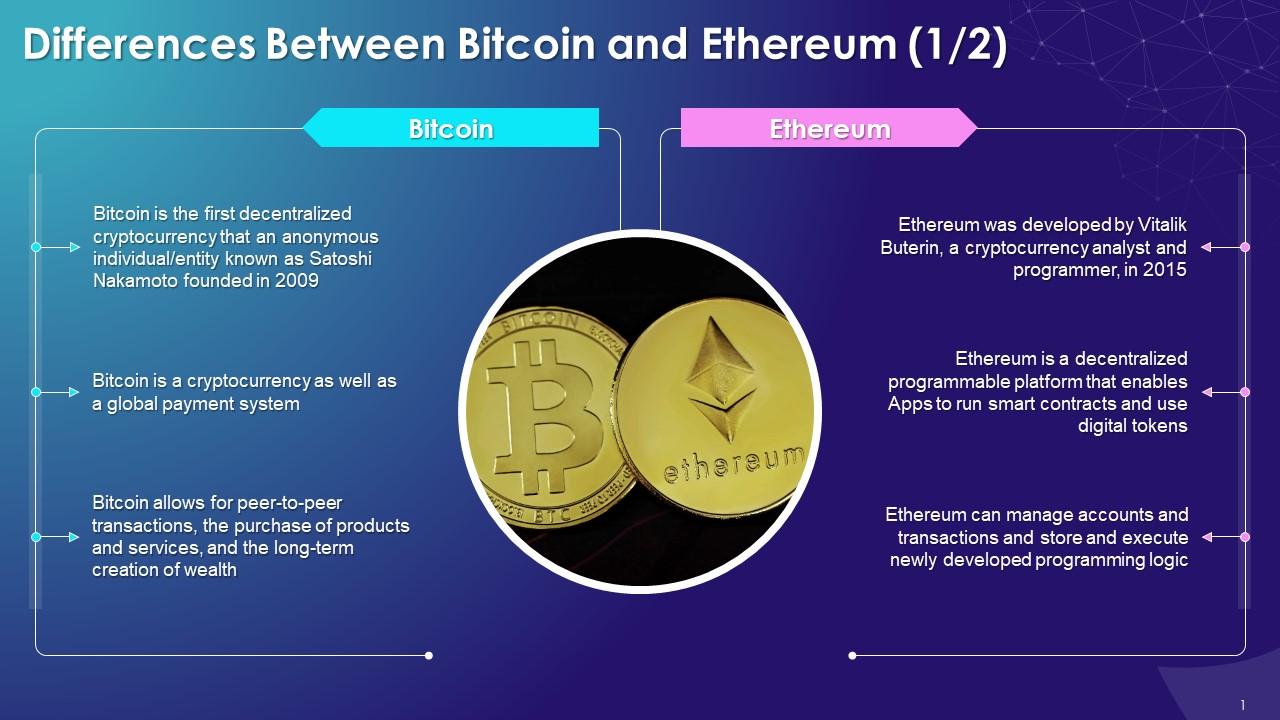
Ethereum and Bitcoin are two of the most prominent cryptocurrencies in the digital financial landscape. Bitcoin, launched in 2009 by an anonymous individual or group known as Satoshi Nakamoto, was the first cryptocurrency, designed as a decentralized digital currency that allows peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries. On the other hand, Ethereum was proposed in late 2013 by programmer Vitalik Buterin and went live in 2015.
It introduced a more versatile platform that allows developers to create decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts on its blockchain.While both cryptocurrencies share the fundamental principle of decentralization, they diverge significantly in their technology and applications. Bitcoin primarily serves as a digital store of value and a medium of exchange. In contrast, Ethereum’s capabilities extend beyond mere transactions, enabling a wide range of applications, including decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
In terms of market position, Bitcoin remains the largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, whereas Ethereum holds a strong second position, constantly innovating and expanding its use cases.
Current Pricing of Ethereum and Bitcoin

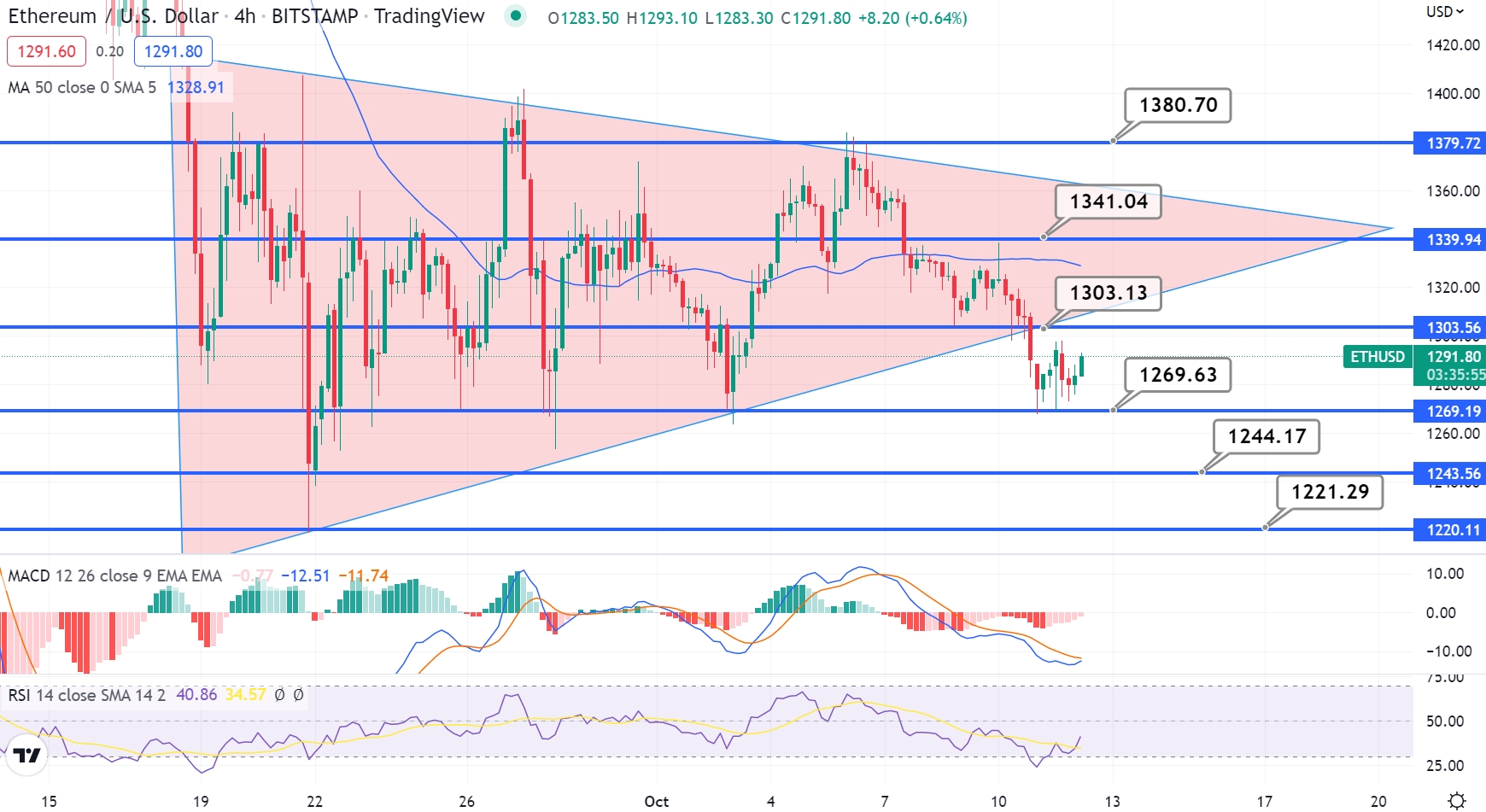
As of today, Bitcoin's price is approximately $60,000, while Ethereum is trading around $4,000. These prices fluctuate constantly due to market dynamics. Over the past year, Bitcoin has seen a significant increase from around $30,000, while Ethereum has surged from approximately $2,000. This steep rise can be attributed to growing institutional interest, increased adoption of cryptocurrencies, and advancements in blockchain technology.Several factors influence the price movements of both cryptocurrencies, including market sentiment, global economic conditions, and regulatory news.
Bitcoin and Ethereum often experience price variations in response to macroeconomic trends, such as inflation rates, interest rate changes, and technological advancements.
Comparing Ethereum and Bitcoin Prices
To better understand the price dynamics of Ethereum and Bitcoin over the past month, here’s a comparative table that illustrates their fluctuations:
| Date | Bitcoin Price (USD) | Ethereum Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 30 Days Ago | $55,000 | $3,500 |
| 15 Days Ago | $58,000 | $3,800 |
| Today | $60,000 | $4,000 |
Recent price changes can be attributed to various factors, including market reactions to regulatory announcements and technological upgrades. For instance, Bitcoin's price rose sharply following news of major corporations accepting it as a payment method. Ethereum’s price surged after updates regarding the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, which aims to improve scalability and reduce transaction fees.Future price predictions suggest:
- Bitcoin may reach $70,000 by the end of the year due to increased institutional adoption.
- Ethereum could potentially hit $5,000, driven by growth in the DeFi and NFT markets.
- Overall market trends indicate volatility but a general upward trajectory for both cryptocurrencies.
Investment Considerations for Ethereum and Bitcoin
Investing in cryptocurrencies like Ethereum and Bitcoin carries both risks and rewards. Bitcoin is often viewed as a digital gold, offering a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation. Conversely, Ethereum presents unique opportunities given its platform's versatility, enabling innovative applications that extend beyond currency use.Before investing, potential investors should consider several factors:
- Volatility: Both cryptocurrencies are known for their price volatility, which can result in significant gains or losses.
- Regulatory Changes: Legislation can dramatically affect market conditions and prices.
- Market Sentiment: News and public perception play crucial roles in price movements.
Common misconceptions about investing in these cryptocurrencies include:
- Bitcoin is the only cryptocurrency worth investing in.
- Investing in cryptocurrencies is guaranteed to yield high returns.
- All cryptocurrencies function the same way; there are notable differences in technology and purpose.
Market Influences on Ethereum and Bitcoin Prices
Market sentiment significantly impacts Ethereum and Bitcoin prices. Positive sentiment can drive prices up, while negative news can lead to sharp declines. For example, announcements from prominent financial institutions regarding Bitcoin acceptance often result in price increases.Global events and regulations also play a pivotal role in influencing the cryptocurrency market. Events such as the COVID-19 pandemic have triggered massive financial stimulus, leading some investors to flock to cryptocurrencies.
Regulatory changes in countries like China have historically led to drastic price drops.Specific events that caused price fluctuations include:
- The announcement of Tesla accepting Bitcoin for purchases, which led to a price spike.
- China's crackdown on cryptocurrency mining, resulting in a price dip.
Future Outlook for Ethereum and Bitcoin

Upcoming technological advancements like Ethereum's transition to proof-of-stake (PoS) are expected to enhance its scalability and energy efficiency, potentially driving prices higher. Bitcoin, on the other hand, may benefit from developments like the Lightning Network, designed to facilitate faster transactions.Institutional investment is poised to have a significant impact on the future prices of both cryptocurrencies. Major financial firms have begun incorporating cryptocurrencies into their portfolios, which could lead to increased demand.The following table summarizes predicted price developments for Ethereum and Bitcoin over the next few years:
| Year | Bitcoin Prediction (USD) | Ethereum Prediction (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | $80,000 | $6,000 |
| 2025 | $100,000 | $10,000 |
Overall, both Ethereum and Bitcoin are positioned for potential growth, driven by technological advancements and increasing market participation.
Last Recap
In summary, the journey through the world of Ethereum and Bitcoin pricing reveals intricate market influences and potential investment opportunities. By staying informed about their price movements, technological advancements, and market sentiment, investors can make more educated decisions in the ever-evolving cryptocurrency landscape.
FAQ Summary
What factors influence the price of Ethereum and Bitcoin?
Key factors include market sentiment, regulatory news, technological advancements, and macroeconomic events.
How do Ethereum and Bitcoin differ in terms of technology?
Ethereum supports smart contracts and decentralized applications, while Bitcoin primarily functions as digital gold and a store of value.
What are the risks of investing in Ethereum and Bitcoin?
Risks include market volatility, regulatory changes, technological flaws, and potential security vulnerabilities.
How can historical price trends help future predictions?
Historical price trends can provide insights into market behavior, helping investors identify potential price movements based on past patterns.
Is now a good time to invest in Ethereum or Bitcoin?
Investment timing depends on individual risk tolerance, market conditions, and personal financial goals. It's essential to conduct thorough research before investing.
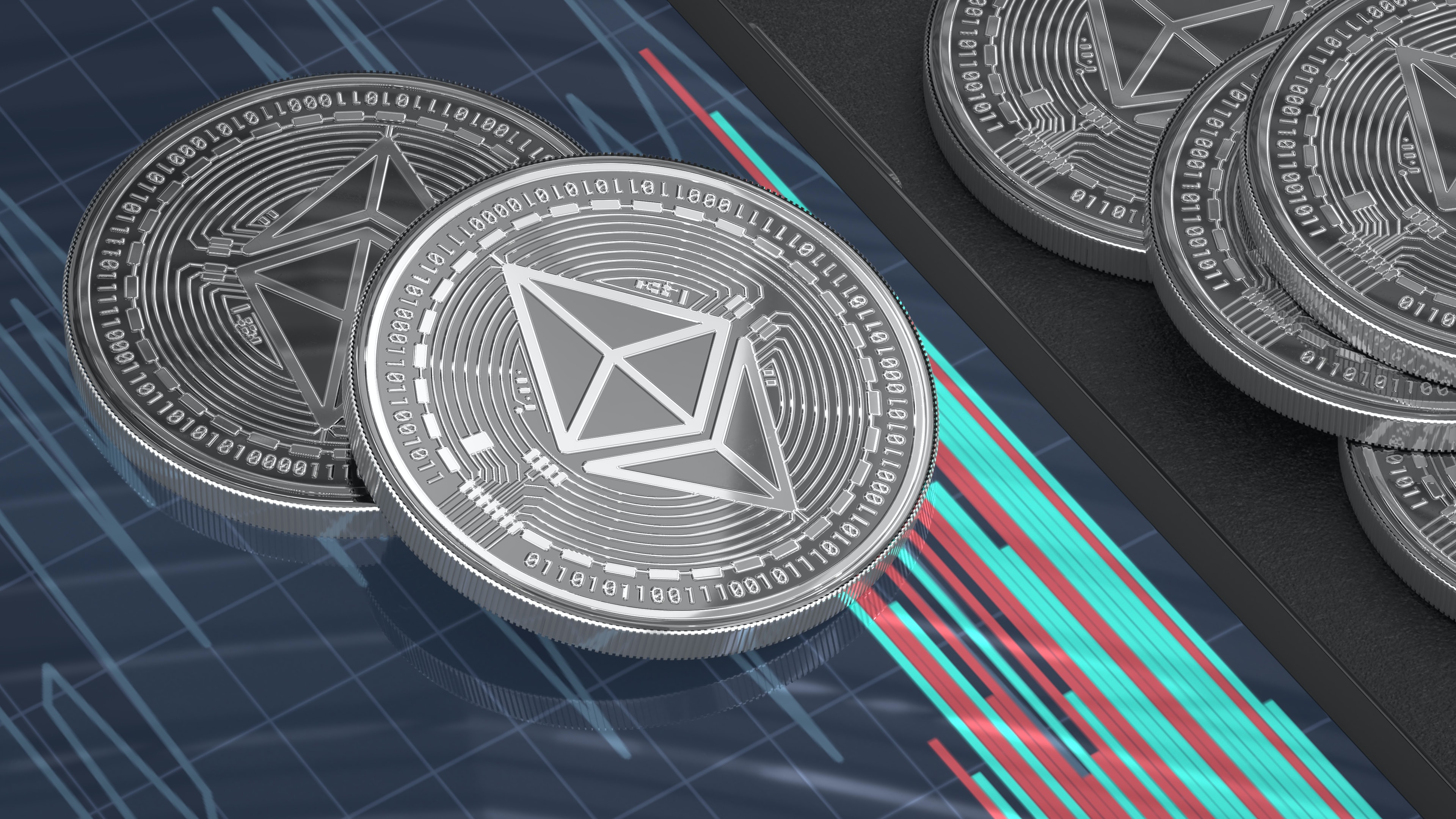










![Overview of blockchain architecture [1]. | Download Scientific Diagram Overview of blockchain architecture [1]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.heliossolutions.co/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Architecture-Of-Blockchain.jpg)