Types Of Blockchain Architecture An Overview Of Types
Types of blockchain architecture are at the forefront of digital innovation today, paving the way for decentralized systems that enhance transparency, security, and efficiency. Understanding these architectures is essential for anyone looking to grasp how blockchain technology can be leveraged across various sectors.
The landscape of blockchain architecture consists of several distinct types, namely public, private, consortium, and hybrid blockchains, each with its unique characteristics and applications. These types not only differ in structure and governance but also in the industries that benefit from their implementation, making it crucial to explore the intricacies of each.
Introduction to Blockchain Architecture
Blockchain architecture refers to the underlying structure that enables the operation of blockchain technology. It plays a significant role in the technology landscape by ensuring data integrity, security, and transparency. Understanding blockchain architecture is essential for grasping how decentralized systems function and how they differ from traditional centralized models. Fundamental components of blockchain architecture include nodes, ledgers, and consensus mechanisms, all of which work together to maintain a secure and reliable network.Over time, blockchain architecture has evolved significantly, transitioning from simple models to more complex systems that accommodate various use cases.
The early iterations primarily focused on cryptocurrency transactions, while modern architectures incorporate smart contracts, interoperability, and advanced security protocols to meet the demands of diverse industries.
Types of Blockchain Architecture
There are three main types of blockchain architecture: public, private, and consortium. Each type serves different purposes and has unique characteristics that cater to various industries.
- Public Blockchains: Open to anyone and decentralized, with no single entity controlling the network. Examples include Bitcoin and Ethereum.
- Private Blockchains: Restricted access and operated by a single organization or a group of organizations. Common in enterprises for sensitive data management.
- Consortium Blockchains: Governed by a group of organizations, offering a balance between decentralization and control. Suitable for industries like banking and supply chain management.
Public blockchains thrive in accessibility and decentralization, while private blockchains excel in security and control. Industries such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management benefit from these varying architectures, each tailored to their specific operational needs.
Public Blockchain Architecture
![Overview of blockchain architecture [1]. | Download Scientific Diagram Overview of blockchain architecture [1]. | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.heliossolutions.co/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Architecture-Of-Blockchain.jpg)
Public blockchains are characterized by their open structure and transparency. They function through a network of nodes that validate and record transactions on a shared ledger, allowing anyone to join and participate in the network. The consensus mechanisms that underpin public blockchains, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), are crucial to maintaining the integrity and security of the system.Notable projects utilizing public blockchain architecture include Bitcoin, which employs PoW to secure its network, and Ethereum, which is transitioning towards PoS for improved efficiency and scalability.
These projects have revolutionized how we perceive currency and decentralized applications.
Private Blockchain Architecture
Private blockchains are designed for specific organizations that require a secure environment for their data and transactions. They feature restricted access, meaning only authorized users can participate in the network. This architecture is ideal for businesses that prioritize confidentiality and compliance with regulatory requirements.Security features in private blockchain architectures include robust access controls, encryption, and identity management systems. Scenarios where private blockchains are preferable over public ones include financial institutions managing sensitive customer data and healthcare organizations handling patient records.
Consortium Blockchain Architecture
Consortium blockchains operate under a collaborative framework involving multiple organizations. These blockchains are governed by predefined rules, allowing participants to share control over the network while maintaining their own privacy and security.The governance model of consortium blockchains is typically established through a voting mechanism, where decisions are made collectively by the participating organizations. This structure fosters trust and collaboration among members, making consortium blockchains advantageous for industries like banking, where multiple entities must work together securely.
Hybrid Blockchain Architecture
Hybrid blockchains combine elements of both public and private blockchains, offering the best of both worlds. They allow organizations to maintain control over sensitive data while still benefiting from the transparency and security of public blockchains.By integrating public and private features, hybrid blockchains can address complex use cases, such as supply chain management, where visibility is crucial, but certain information must remain confidential.
Real-world applications of hybrid blockchain architecture include projects in healthcare and logistics, where stakeholders need shared access to data without compromising privacy.
Key Components of Blockchain Architecture
The essential components of blockchain architecture include nodes, ledgers, and smart contracts. Nodes are the individual devices that participate in the network, while the ledger is the database that stores all transaction records. Smart contracts automate processes by executing predefined conditions without the need for intermediaries.Cryptography plays a vital role in ensuring security within blockchain systems. Techniques such as hashing and encryption protect data from unauthorized access and tampering.
Here’s a comparison of key component functions across different blockchain types:
| Component | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain | Consortium Blockchain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nodes | Open to all | Authorized participants only | Member-controlled |
| Ledger | Transparent and decentralized | Restricted access | Shared among members |
| Smart Contracts | Widely used | Customizable for internal use | Defined by consortium rules |
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain Architectures
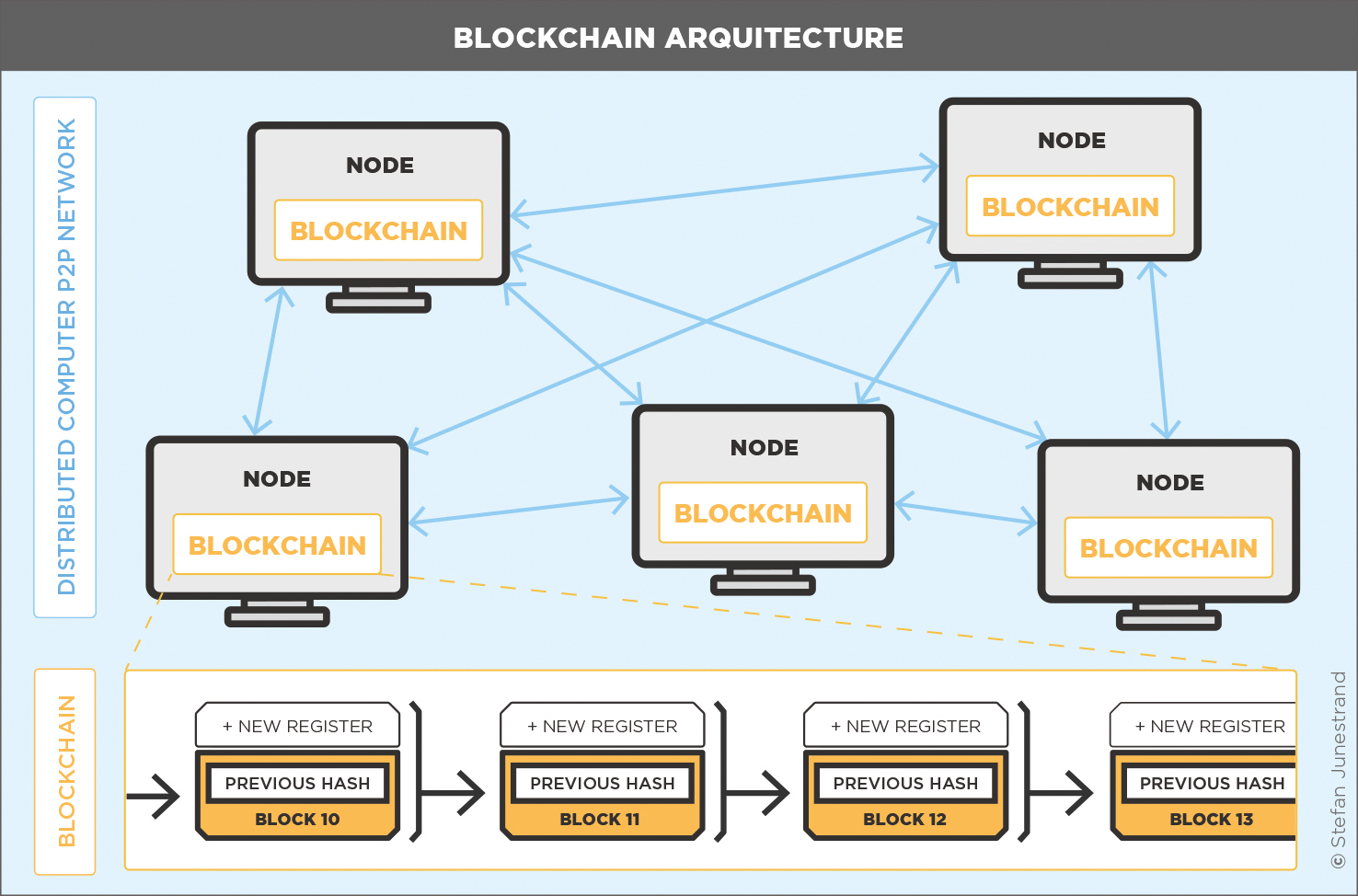
Different types of blockchain architectures face common challenges, including scalability issues, interoperability between different blockchain systems, and regulatory compliance. These challenges can hinder widespread adoption and limit the potential of blockchain technology.To overcome these limitations, organizations can adopt strategies such as layer-two solutions to enhance scalability, standardization efforts to improve interoperability, and proactive engagement with regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and build trust.
Future Trends in Blockchain Architecture
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, several emerging trends are shaping its future architecture. The integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is expected to enhance blockchain functionality and expand its applications.Anticipated developments in blockchain architecture over the next decade include:
- Increased adoption of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
- Enhanced security measures through quantum-resistant algorithms.
- Integration of AI for automated decision-making in smart contracts.
- Interoperable blockchains enabling cross-chain transactions.
- Greater emphasis on sustainability and energy efficiency in blockchain operations.
Closing Notes
In summary, the exploration of types of blockchain architecture reveals a rich tapestry of possibilities that can transform industries and enhance operational efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about these architectures will empower organizations to choose the right solution for their specific needs.
Detailed FAQs
What is blockchain architecture?
Blockchain architecture refers to the structure and design of a blockchain system, including its components, protocols, and interactions.
What are the main differences between public and private blockchains?
Public blockchains are open to everyone and promote decentralization, while private blockchains restrict access to a specific group, focusing on security and control.
What industries benefit from blockchain architecture?
Industries like finance, supply chain, healthcare, and real estate leverage blockchain architecture for improved transparency, security, and efficiency.
Are hybrid blockchains popular?
Yes, hybrid blockchains are gaining popularity as they combine the benefits of both public and private blockchains, making them versatile for various applications.
What are some challenges faced by blockchain architectures?
Common challenges include scalability issues, regulatory hurdles, and interoperability among different blockchain systems.


